Nội dung bài viết
Trong thế giới ngôn ngữ, việc truyền đạt lại lời nói của người khác một cách chính xác và hiệu quả là một kỹ năng thiết yếu. Đặc biệt, trong tiếng Anh, câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh (Reported Speech hoặc Indirect Speech) không chỉ là một cấu trúc ngữ pháp quan trọng mà còn là một công cụ giao tiếp mạnh mẽ, giúp bạn tường thuật lại thông tin một cách lịch sự, linh hoạt và phù hợp với ngữ cảnh. Việc nắm vững cách chuyển đổi từ câu trực tiếp sang gián tiếp không chỉ cải thiện khả năng viết và nói mà còn thể hiện sự tinh tế trong việc sử dụng ngôn ngữ. Bài viết này của Trường Nguyễn Bỉnh Khiêm sẽ đi sâu vào mọi khía cạnh của câu nói gián tiếp, từ những nguyên tắc cơ bản nhất đến các trường hợp đặc biệt, giúp bạn tự tin vận dụng cấu trúc này trong mọi tình huống.
Khái niệm và tầm quan trọng của câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh
Hiểu rõ về câu nói gián tiếp bắt đầu từ việc phân biệt nó với câu nói trực tiếp, cũng như nhận thức được vai trò không thể thiếu của nó trong giao tiếp tiếng Anh hàng ngày và trong các văn bản học thuật. Nắm vững hai khái niệm này là bước đệm quan trọng để bạn có thể chinh phục mọi quy tắc chuyển đổi phức tạp hơn sau này.
Câu nói trực tiếp là gì?
Câu nói trực tiếp (Direct Speech) là cách chúng ta lặp lại chính xác từng lời, từng chữ của người nói ban đầu. Khi sử dụng câu trực tiếp, người viết hoặc người nói thường đặt lời nói đó trong dấu ngoặc kép (” “) và đi kèm với một động từ tường thuật như “said”, “asked”, “replied” để chỉ rõ nguồn gốc của lời nói. Ví dụ, nếu một người nói “I am busy now,” thì khi tường thuật trực tiếp, chúng ta sẽ nói: She said, “I am busy now.” Dạng câu này giữ nguyên thì, đại từ, và các trạng từ chỉ thời gian, địa điểm như trong lời nói gốc.
Câu nói gián tiếp là gì?
Ngược lại, câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh (Indirect Speech hoặc Reported Speech) là cách chúng ta thuật lại ý chính hoặc nội dung của lời nói gốc mà không lặp lại chính xác từng từ. Khi chuyển sang câu gián tiếp, chúng ta thường phải thay đổi thì của động từ, các đại từ nhân xưng, tính từ sở hữu và các trạng từ chỉ thời gian, địa điểm để phù hợp với thời điểm và địa điểm tường thuật. Dấu ngoặc kép sẽ bị loại bỏ và thường có thêm liên từ “that” (có thể lược bỏ) sau động từ tường thuật. Ví dụ, câu “I am busy now” khi chuyển sang gián tiếp sẽ thành: She said that she was busy then. Mục đích của câu gián tiếp là để tích hợp lời nói của người khác vào câu chuyện của chúng ta một cách tự nhiên và mạch lạc hơn.
Tại sao cần dùng câu nói gián tiếp?
Sử dụng câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh mang lại nhiều lợi ích quan trọng trong giao tiếp. Thứ nhất, nó giúp tránh sự lặp lại lời nói nguyên văn, làm cho đoạn văn hoặc cuộc hội thoại trở nên trôi chảy và dễ đọc/nghe hơn. Thay vì ngắt quãng bằng những dấu ngoặc kép, lời nói gián tiếp tích hợp thông tin một cách liền mạch. Thứ hai, nó cho phép chúng ta thay đổi góc nhìn từ người nói ban đầu sang người tường thuật, giúp điều chỉnh thông tin cho phù hợp với ngữ cảnh hiện tại. Ví dụ, nếu bạn kể lại một cuộc trò chuyện từ hôm qua, việc thay đổi thì và trạng từ sẽ giúp người nghe hiểu rõ rằng sự kiện đó đã xảy ra trong quá khứ. Cuối cùng, câu nói gián tiếp thường được xem là lịch sự và khách quan hơn, đặc biệt khi bạn muốn tóm tắt hoặc trình bày lại ý kiến của người khác mà không cần phải cam kết về tính chính xác tuyệt đối của từng từ ngữ họ đã dùng. Điều này đặc biệt hữu ích trong các bài viết báo cáo, nghiên cứu hoặc các tình huống giao tiếp trang trọng.
Các nguyên tắc cơ bản khi chuyển từ câu trực tiếp sang gián tiếp
Việc chuyển đổi từ câu trực tiếp sang câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh đòi hỏi sự tuân thủ một số nguyên tắc cơ bản. Những nguyên tắc này bao gồm lùi thì của động từ, thay đổi trạng từ chỉ thời gian và địa điểm, cũng như điều chỉnh đại từ nhân xưng và tính từ sở hữu. Nắm vững các quy tắc này là chìa khóa để tạo ra những câu gián tiếp chính xác và tự nhiên.
Lùi thì (Backshift of Tenses)
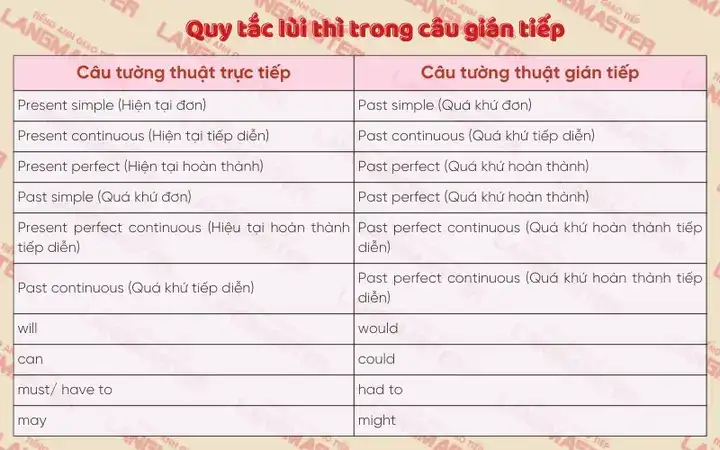
Lùi thì là quy tắc quan trọng nhất khi chuyển từ câu trực tiếp sang câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh, đặc biệt khi động từ tường thuật (reporting verb) ở thì quá khứ (ví dụ: said, asked, told). Ý tưởng là động từ trong mệnh đề được tường thuật sẽ “lùi” về một thì trong quá khứ so với thì gốc.
Bảng tóm tắt các thì khi lùi:
| Thì của câu trực tiếp | Thì của câu gián tiếp | Ví dụ (trực tiếp -> gián tiếp) || :———————– | :————————– | :————————————————————————————————————————————— || Hiện tại đơn | Quá khứ đơn | He said, “I am happy.” -> He said that he was happy. || Hiện tại tiếp diễn | Quá khứ tiếp diễn | She said, “I am working.” -> She said that she was working. || Hiện tại hoàn thành | Quá khứ hoàn thành | They said, “We have finished the task.” -> They said that they had finished the task. || Hiện tại hoàn thành tiếp diễn | Quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn | He said, “I have been studying for hours.” -> He said that he had been studying for hours. || Quá khứ đơn | Quá khứ hoàn thành | She said, “I went to the cinema.” -> She said that she had gone to the cinema. || Quá khứ tiếp diễn | Quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn | He said, “I was reading a book.” -> He said that he had been reading a book. || Tương lai đơn | Tương lai trong quá khứ | They said, “We will go tomorrow.” -> They said that they would go the next day. || Tương lai tiếp diễn | Tương lai tiếp diễn trong quá khứ | She said, “I will be waiting.” -> She said that she would be waiting. |
Trường hợp không lùi thì:
Mặc dù quy tắc lùi thì là phổ biến, có một số trường hợp đặc biệt mà chúng ta không cần lùi thì của động từ trong câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh:
- Sự thật hiển nhiên, chân lý, quy luật khoa học: Nếu lời nói trực tiếp diễn tả một sự thật luôn đúng, chúng ta giữ nguyên thì.
- Direct: The teacher said, “The Earth revolves around the sun.”
- Indirect: The teacher said that the Earth revolves around the sun.
- Động từ tường thuật ở thì hiện tại hoặc tương lai: Nếu động từ tường thuật (say, tell, ask) không ở thì quá khứ, thì trong mệnh đề gián tiếp sẽ không thay đổi.
- Direct: He says, “I am tired.”
- Indirect: He says that he is tired.
- Câu điều kiện loại 2 và 3: Các thì trong mệnh đề điều kiện loại 2 và 3 thường không thay đổi.
- Direct: She said, “If I were rich, I would travel the world.”
- Indirect: She said that if she were rich, she would travel the world.
- Khi câu gián tiếp tường thuật một sự việc vẫn đúng ở thời điểm nói:
- Direct: He said, “My name is John.”
- Indirect: He said that his name is John. (Nếu tên anh ấy vẫn là John)
Việc nắm vững cả quy tắc lùi thì và các trường hợp ngoại lệ sẽ giúp bạn sử dụng câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh một cách linh hoạt và chính xác.
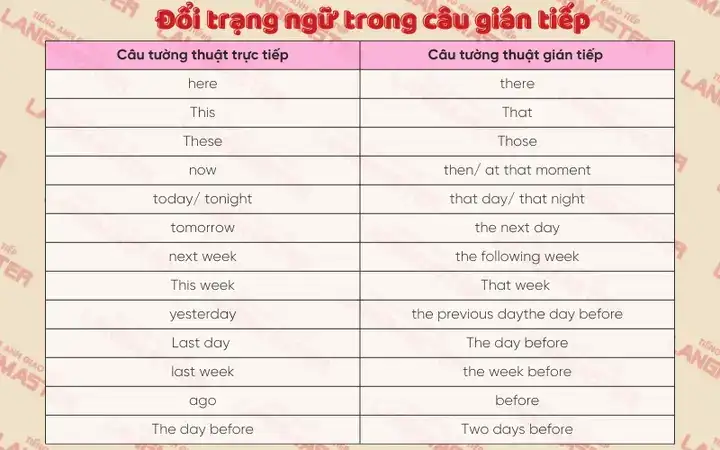
Thay đổi trạng từ chỉ thời gian và địa điểm
Ngoài việc lùi thì, một nguyên tắc quan trọng khác khi chuyển từ câu trực tiếp sang câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh là thay đổi các trạng từ hoặc cụm trạng từ chỉ thời gian và địa điểm để phản ánh đúng ngữ cảnh của thời điểm tường thuật. Điều này là cần thiết vì thời điểm và địa điểm lời nói được tường thuật thường khác với thời điểm và địa điểm lời nói gốc.
Bảng tóm tắt các thay đổi phổ biến:
| Từ/Cụm từ trong câu trực tiếp | Từ/Cụm từ trong câu gián tiếp | Ví dụ (trực tiếp -> gián tiếp) || :—————————- | :—————————— | :—————————————————————————————————————————————— || now | then, at that time | He said, “I am busy now.” -> He said that he was busy then. || today | that day | She said, “I will leave today.” -> She said that she would leave that day. || tonight | that night | They said, “We are staying in tonight.” -> They said that they were staying in that night. || yesterday | the day before, the previous day | He said, “I saw her yesterday.” -> He said that he had seen her the day before. || last night/week/month/year | the night/week/month/year before, the previous night/week/month/year | She said, “I visited her last week.” -> She said that she had visited her the previous week. || tomorrow | the next day, the following day | He said, “I will call you tomorrow.” -> He said that he would call me the next day. || next week/month/year | the next week/month/year, the following week/month/year | They said, “We will move next month.” -> They said that they would move the following month. || here | there | She said, “Put it here.” -> She said to put it there. || this | that | He said, “I want this book.” -> He said that he wanted that book. || these | those | She said, “I like these flowers.” -> She said that she liked those flowers. || ago | before | He said, “I arrived two hours ago.” -> He said that he had arrived two hours before. |
Ví dụ minh họa:
- Direct: Mary said, “I’m going to London tomorrow.”
- Indirect: Mary said that she was going to London the next day.
- Direct: My boss said, “The meeting is here at 10 AM today.”
- Indirect: My boss said that the meeting was there at 10 AM that day.
Việc thay đổi trạng từ không chỉ đảm bảo ngữ pháp chính xác mà còn giúp người nghe/đọc dễ dàng hiểu được ngữ cảnh thời gian và địa điểm của lời nói được tường thuật.
Thay đổi đại từ nhân xưng và tính từ sở hữu
Một nguyên tắc cơ bản khác khi chuyển từ câu trực tiếp sang câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh là điều chỉnh các đại từ nhân xưng (I, you, he, she, it, we, they) và tính từ sở hữu (my, your, his, her, its, our, their). Các thay đổi này phụ thuộc vào người nói, người nghe trong câu trực tiếp và người tường thuật trong câu gián tiếp. Mục đích là để đảm bảo rằng các đại từ và tính từ sở hữu phản ánh đúng đối tượng được nhắc đến trong ngữ cảnh của lời nói gián tiếp.
Quy tắc chung:
- Đại từ ngôi thứ nhất (I, we, my, our): Thay đổi theo chủ ngữ của động từ tường thuật.
- Direct: He said, “I am tired.”
- Indirect: He said that he was tired.
- Direct: They said, “Our car is broken.”
- Indirect: They said that their car was broken.
- Đại từ ngôi thứ hai (you, your): Thay đổi theo tân ngữ của động từ tường thuật (nếu có) hoặc theo ngữ cảnh chung.
- Direct: He said to me, “You look great.”
- Indirect: He told me that I looked great.
- Direct: She asked, “Do you like coffee?” (Giả sử cô ấy hỏi tôi)
- Indirect: She asked if I liked coffee.
- Đại từ ngôi thứ ba (he, she, it, they, his, her, its, their): Thường giữ nguyên, vì chúng đã ở ngôi thứ ba.
- Direct: She said, “He is a good student.”
- Indirect: She said that he was a good student.
- Direct: John said, “His project is ready.”
- Indirect: John said that his project was ready.
Ví dụ minh họa chi tiết:
- Direct: Sarah said to Mark, “I will meet you at your house.”
- Ở đây, “I” là Sarah, “you” là Mark, “your” là của Mark.
- Indirect: Sarah told Mark that she would meet him at his house.
- Direct: My parents said, “We are proud of you, son.” (Họ nói với con trai họ)
- Indirect: My parents told their son that they were proud of him.
Việc thay đổi đại từ và tính từ sở hữu đòi hỏi sự cẩn trọng để tránh nhầm lẫn về đối tượng được nhắc đến. Luôn tự hỏi “ai đang nói về ai” trong ngữ cảnh gián tiếp để đảm bảo tính chính xác.
Thay đổi động từ khuyết thiếu (Modal Verbs)
Khi chuyển câu có động từ khuyết thiếu (modal verbs) từ trực tiếp sang câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh, chúng ta cũng cần thực hiện một số thay đổi nhất định. Giống như các động từ chính, động từ khuyết thiếu cũng thường “lùi” về dạng quá khứ của chúng.
Bảng tóm tắt các thay đổi phổ biến:
| Động từ khuyết thiếu trong câu trực tiếp | Động từ khuyết thiếu trong câu gián tiếp | Ví dụ (trực tiếp -> gián tiếp) || :————————————— | :————————————— | :———————————————————————————————————————————————– || will | would | He said, “I will help you.” -> He said that he would help me. || can | could | She said, “I can swim.” -> She said that she could swim. || may | might | He said, “It may rain.” -> He said that it might rain. || must | had to | They said, “We must leave now.” -> They said that they had to leave then. (Hoặc đôi khi giữ nguyên ‘must’ nếu là nghĩa vụ bắt buộc) || shall (trong câu hỏi hoặc đề nghị) | should, would | He asked, “Where shall I go?” -> He asked where he should go. || ought to | ought to (giữ nguyên) | She said, “You ought to study harder.” -> She said that I ought to study harder. || could, would, should, might, had better | (thường giữ nguyên) | He said, “I could do it.” -> He said that he could do it. || need (trong phủ định/nghi vấn) | didn’t need to | She said, “You needn’t worry.” -> She said that I didn’t need to worry. |
Lưu ý quan trọng về “Must”:* Khi “must” diễn tả sự bắt buộc, nghĩa vụ cần làm (obligation), nó thường được đổi thành had to.* Direct: He said, “I must finish this report by Friday.”* Indirect: He said that he had to finish that report by Friday.* Tuy nhiên, khi “must” diễn tả sự suy luận hợp lý, một phỏng đoán chắc chắn (logical deduction), nó thường được giữ nguyên.* Direct: She said, “He must be very tired after such a long journey.”* Indirect: She said that he must be very tired after such a long journey.
Việc hiểu rõ cách thay đổi các động từ khuyết thiếu là một phần không thể thiếu để làm chủ cấu trúc câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh. Hãy luôn xem xét ngữ cảnh của câu trực tiếp để chọn động từ khuyết thiếu gián tiếp phù hợp nhất.
Cấu trúc câu nói gián tiếp theo từng loại câu
Mỗi loại câu trong tiếng Anh – trần thuật, câu hỏi, mệnh lệnh, và cảm thán – đều có những quy tắc chuyển đổi riêng khi biến thành câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh. Việc nắm vững từng cấu trúc này là chìa khóa để tường thuật lại lời nói một cách chính xác và hiệu quả.
Câu trần thuật (Statements)
Chuyển đổi câu trần thuật từ trực tiếp sang câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh là dạng phổ biến và cơ bản nhất. Cấu trúc và các bước thay đổi tương đối đơn giản.
Cấu trúc chung:
S + say/tell + (O) + (that) + S + V (lùi thì)
- S: Chủ ngữ của câu tường thuật.
- say/tell: Động từ tường thuật. Sử dụng “say” khi không có tân ngữ đi kèm (người nghe), và “tell” khi có tân ngữ (người nghe).
- (O): Tân ngữ (người nghe).
- (that): Liên từ “that” có thể được thêm vào sau động từ tường thuật, nhưng thường có thể lược bỏ, đặc biệt trong giao tiếp thân mật.
- S + V (lùi thì): Mệnh đề gián tiếp, với chủ ngữ và động từ đã được thay đổi theo các nguyên tắc lùi thì, đại từ, và trạng từ đã học.
Ví dụ đa dạng:
- Direct: He said, “I am reading a book.”
- Indirect: He said (that) he was reading a book.
- Direct: She told me, “I have finished my homework.”
- Indirect: She told me (that) she had finished her homework.
- Direct: They said, “We will go to the party tomorrow.”
- Indirect: They said (that) they would go to the party the next day.
- Direct: My mother said, “You must eat your vegetables.”
- Indirect: My mother said (that) I had to eat my vegetables.
- Direct: John said, “I can’t come to the meeting on Monday.”
- Indirect: John said (that) he couldn’t come to the meeting on Monday.
- Direct: The student said, “I don’t understand this lesson.”
- Indirect: The student said (that) he didn’t understand that lesson.
- Direct: My friend said, “I saw your brother yesterday.”
- Indirect: My friend said (that) she had seen my brother the day before.
- Direct: The old man said, “Life is full of surprises.” (Sự thật hiển nhiên)
- Indirect: The old man said (that) life is full of surprises.
- Direct: Sarah said to Peter, “I will call you later.”
- Indirect: Sarah told Peter (that) she would call him later.
- Direct: The doctor said, “You should get more rest.”
- Indirect: The doctor said (that) I should get more rest.
Khi chuyển câu trần thuật sang gián tiếp, hãy luôn nhớ kiểm tra ba yếu tố chính: thì của động từ, đại từ nhân xưng/tính từ sở hữu, và trạng từ chỉ thời gian/địa điểm. Điều này đảm bảo câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh của bạn chính xác và tự nhiên.
Câu hỏi (Questions)
Chuyển câu hỏi từ trực tiếp sang câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh đòi hỏi một số quy tắc đặc biệt, khác với câu trần thuật. Quan trọng nhất là không còn dấu hỏi và trật tự từ sẽ giống như câu trần thuật (chủ ngữ đứng trước động từ).
Câu hỏi Yes/No
Đây là những câu hỏi mà câu trả lời chỉ có thể là “Yes” hoặc “No”.
Cấu trúc: S + ask/wonder/want to know + if/whether + S + V (lùi thì)
- S: Chủ ngữ của câu tường thuật.
- ask/wonder/want to know: Động từ tường thuật.
- if/whether: Từ nối bắt buộc, thay thế cho dấu hỏi và thể hiện ý nghĩa của câu hỏi Yes/No. “Whether” thường được dùng trong các tình huống trang trọng hơn hoặc khi có hai lựa chọn.
- S + V (lùi thì): Mệnh đề gián tiếp với trật tự từ của câu trần thuật (không đảo ngữ) và động từ đã lùi thì cùng các thay đổi về đại từ, trạng từ.
Ví dụ đa dạng:
- Direct: He asked, “Are you busy?”
- Indirect: He asked if I was busy.
- Direct: She asked me, “Do you like coffee?”
- Indirect: She asked me if I liked coffee.
- Direct: My mother asked, “Did you finish your homework?”
- Indirect: My mother asked whether I had finished my homework.
- Direct: The teacher asked, “Have you studied for the exam?”
- Indirect: The teacher asked if I had studied for the exam.
- Direct: John asked, “Will you come to the party tomorrow?”
- Indirect: John asked if I would come to the party the next day.
- Direct: Mary asked, “Can you help me?”
- Indirect: Mary asked if I could help her.
- Direct: They asked us, “Are you enjoying the show?”
- Indirect: They asked us if we were enjoying the show.
- Direct: He wondered, “Is it going to rain?”
- Indirect: He wondered whether it was going to rain.
- Direct: The police officer asked, “Do you have any identification?”
- Indirect: The police officer asked if I had any identification.
- Direct: Sarah asked, “Were you at home last night?”
- Indirect: Sarah asked if I had been at home the previous night.
Câu hỏi Wh-
Đây là những câu hỏi bắt đầu bằng các từ để hỏi như “who, what, where, when, why, how”.
Cấu trúc: S + ask/wonder/want to know + Wh-word + S + V (lùi thì)
- S: Chủ ngữ của câu tường thuật.
- ask/wonder/want to know: Động từ tường thuật.
- Wh-word: Từ để hỏi (who, what, where, etc.) được giữ nguyên và đóng vai trò là từ nối.
- S + V (lùi thì): Mệnh đề gián tiếp với trật tự từ của câu trần thuật (không đảo ngữ) và động từ đã lùi thì cùng các thay đổi về đại từ, trạng từ.
Ví dụ đa dạng:
- Direct: He asked, “What are you doing?”
- Indirect: He asked what I was doing.
- Direct: She asked, “Where do you live?”
- Indirect: She asked where I lived.
- Direct: My father asked, “When will you come home?”
- Indirect: My father asked when I would come home.
- Direct: The detective asked, “Who broke the window?”
- Indirect: The detective asked who had broken the window.
- Direct: John asked, “Why did you leave early?”
- Indirect: John asked why I had left early.
- Direct: Sarah asked, “How often do you exercise?”
- Indirect: Sarah asked how often I exercised.
- Direct: They asked me, “Which book did you choose?”
- Indirect: They asked me which book I had chosen.
- Direct: He wondered, “What time is it?”
- Indirect: He wondered what time it was.
- Direct: The tourist asked, “How can I get to the station?”
- Indirect: The tourist asked how he could get to the station.
- Direct: My friend asked, “Whose car is that?”
- Indirect: My friend asked whose car that was.
Khi chuyển câu hỏi sang câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh, hãy nhớ rằng bạn đang tường thuật một câu hỏi, không phải đặt một câu hỏi mới. Do đó, trật tự từ phải là chủ ngữ + động từ, và không có dấu hỏi chấm ở cuối.
Câu mệnh lệnh, yêu cầu, đề nghị (Commands, Requests, Suggestions)
Khi chuyển câu mệnh lệnh, yêu cầu, hoặc đề nghị từ trực tiếp sang câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh, chúng ta thường không lùi thì mà thay đổi cấu trúc của động từ. Các động từ tường thuật như “tell,” “ask,” “order,” “advise,” “suggest” đóng vai trò quan trọng trong việc thể hiện sắc thái của lời nói gốc.
Mệnh lệnh khẳng định
Cấu trúc: S + ask/tell/order + O + to V (nguyên mẫu)
- S: Chủ ngữ của câu tường thuật.
- ask/tell/order: Động từ tường thuật, tùy thuộc vào mức độ của mệnh lệnh (từ yêu cầu nhẹ nhàng đến ra lệnh).
- O: Tân ngữ (người nhận mệnh lệnh).
- to V: Dạng động từ nguyên mẫu có “to”.
Ví dụ đa dạng:
- Direct: He said to me, “Close the door.”
- Indirect: He told me to close the door.
- Direct: The teacher said to the students, “Listen carefully.”
- Indirect: The teacher told the students to listen carefully.
- Direct: My mother said, “Clean your room!”
- Indirect: My mother ordered me to clean my room.
- Direct: The doctor said to the patient, “Take this medicine three times a day.”
- Indirect: The doctor advised the patient to take that medicine three times a day.
- Direct: He said to her, “Wait for me.”
- Indirect: He asked her to wait for him.
Mệnh lệnh phủ định
Cấu trúc: S + ask/tell/order + O + not to V (nguyên mẫu)
- Tương tự cấu trúc khẳng định, nhưng thêm “not” trước “to V”.
Ví dụ đa dạng:
- Direct: He said to me, “Don’t touch that!”
- Indirect: He told me not to touch that.
- Direct: The teacher said to the students, “Don’t make noise.”
- Indirect: The teacher told the students not to make noise.
- Direct: My father said, “Don’t play with fire.”
- Indirect: My father warned me not to play with fire.
- Direct: She said to him, “Don’t forget to call me.”
- Indirect: She reminded him not to forget to call her.
- Direct: The police officer said to the driver, “Don’t park here.”
- Indirect: The police officer ordered the driver not to park there.
Đề nghị, lời khuyên
Đối với đề nghị hoặc lời khuyên, có nhiều cấu trúc động từ tường thuật khác nhau tùy thuộc vào sắc thái.
Cấu trúc 1 (với V-ing): S + suggest/recommend + V-ing
Ví dụ:
- Direct: He said, “Let’s go to the cinema.”
- Indirect: He suggested going to the cinema.
- Direct: She said, “How about visiting the museum?”
- Indirect: She suggested visiting the museum.
Cấu trúc 2 (với that clause): S + suggest/recommend + (that) + S + (should) + V (nguyên mẫu)
Ví dụ:
- Direct: He said, “You should study harder.”
- Indirect: He suggested (that) I should study harder. (Hoặc He suggested (that) I study harder.)
- Direct: She said, “I think we should try this new restaurant.”
- Indirect: She suggested (that) we should try that new restaurant.
Cấu trúc 3 (với advise): S + advise + O + to V (cho lời khuyên)
Ví dụ:
- Direct: He said to me, “You should see a doctor.”
- Indirect: He advised me to see a doctor.
Việc lựa chọn động từ tường thuật phù hợp (tell, ask, order, advise, suggest, warn, remind, etc.) là rất quan trọng để thể hiện đúng ý nghĩa và ngữ điệu của câu trực tiếp khi chuyển sang câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh.
Câu cảm thán (Exclamations)
Chuyển câu cảm thán từ trực tiếp sang câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh thường liên quan đến việc biến đổi nó thành một câu trần thuật và sử dụng các động từ tường thuật thể hiện cảm xúc. Dấu chấm than (!) sẽ bị loại bỏ.
Cấu trúc chung:
S + exclaim/cry out/remark + (with delight/surprise/anger, etc.) + (that) + S + V (lùi thì)
Hoặc đơn giản hơn: S + exclaim/say + (that) + S + V (lùi thì)
- S: Chủ ngữ của câu tường thuật.
- exclaim/cry out/remark: Các động từ tường thuật thể hiện cảm xúc mạnh mẽ. Bạn cũng có thể dùng say và bổ sung trạng từ.
- (with delight/surprise/anger, etc.): Các cụm trạng từ này có thể được thêm vào để làm rõ cảm xúc của người nói.
- (that): Liên từ “that” thường được sử dụng.
- S + V (lùi thì): Mệnh đề gián tiếp đã được chuyển đổi thành câu trần thuật, với thì động từ lùi và các đại từ/trạng từ được thay đổi.
Lưu ý: Các từ cảm thán như “Oh!”, “Ah!”, “Wow!”, “Alas!”, “Hurrah!” thường bị lược bỏ hoặc được thay thế bằng các động từ hoặc trạng từ tường thuật phù hợp.
Ví dụ đa dạng:
- Direct: He said, “What a beautiful flower!”
- Indirect: He exclaimed (that) it was a beautiful flower.
- (Hoặc: He exclaimed how beautiful the flower was.)
- Direct: She said, “How clever you are!”
- Indirect: She exclaimed (that) I was very clever.
- (Hoặc: She exclaimed how clever I was.)
- Direct: They said, “What a terrible mistake!”
- Indirect: They exclaimed (that) it was a terrible mistake.
- Direct: He said, “Alas! I am ruined!”
- Indirect: He exclaimed sadly (that) he was ruined.
- Direct: She said, “Hurrah! We have won!”
- Indirect: She exclaimed with joy (that) they had won.
- Direct: He said, “Oh! I forgot my keys!”
- Indirect: He exclaimed in surprise (that) he had forgotten his keys.
- Direct: She said, “What a relief!”
- Indirect: She exclaimed (that) it was a great relief.
- Direct: He cried out, “Fire!”
- Indirect: He cried out about a fire. (Hoặc He shouted that there was a fire.)
- Direct: “Ugh, this tastes awful!” he muttered.
- Indirect: He muttered that it tasted awful.
- Direct: “Fantastic! You did it!” she cheered.
- Indirect: She cheered (that) I had done it.
Khi xử lý câu cảm thán, điều quan trọng là phải nhận biết cảm xúc mà lời nói trực tiếp truyền tải và sử dụng động từ tường thuật hoặc trạng từ phù hợp để thể hiện cảm xúc đó trong câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh.
Các động từ tường thuật đặc biệt và cách dùng
Ngoài các động từ tường thuật cơ bản như “say” và “tell,” tiếng Anh còn có một loạt các động từ tường thuật đặc biệt, giúp thể hiện sắc thái, ý định và cảm xúc của người nói một cách chi tiết hơn trong câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh. Việc sử dụng đúng động từ tường thuật sẽ làm cho bài viết hoặc cuộc hội thoại của bạn trở nên sinh động và chính xác hơn.
Với to V (promise, agree, refuse, offer, threaten, decide, etc.)
Một số động từ tường thuật được theo sau bởi cấu trúc to V (động từ nguyên mẫu có to), thường dùng để tường thuật các lời hứa, thỏa thuận, từ chối, đề nghị, đe dọa hoặc quyết định.
- Promise (hứa):
- Direct: He said, “I will call you back.”
- Indirect: He promised to call me back.
- Agree (đồng ý):
- Direct: She said, “Yes, I will help you.”
- Indirect: She agreed to help me.
- Refuse (từ chối):
- Direct: He said, “No, I won’t do that.”
- Indirect: He refused to do that.
- Offer (đề nghị):
- Direct: He said, “Shall I carry your bags?”
- Indirect: He offered to carry my bags.
- Threaten (đe dọa):
- Direct: He said, “I will punish you if you do that again.”
- Indirect: He threatened to punish me if I did that again.
- Decide (quyết định):
- Direct: She said, “I will buy a new car.”
- Indirect: She decided to buy a new car.
- Demand (yêu cầu):
- Direct: The customer said, “I want to speak to the manager.”
- Indirect: The customer demanded to speak to the manager.
- Expect (mong đợi):
- Direct: He said, “I expect to finish by noon.”
- Indirect: He expected to finish by noon.
- Hope (hy vọng):
- Direct: She said, “I hope to pass the exam.”
- Indirect: She hoped to pass the exam.
- Propose (đề xuất):
- Direct: He said, “I propose to start the project next week.”
- Indirect: He proposed to start the project the following week.
Với V-ing (admit, deny, suggest, insist on, apologize for, complain about, etc.)
Một nhóm động từ tường thuật khác được theo sau bởi dạng V-ing, thường dùng để tường thuật các hành động như thừa nhận, phủ nhận, đề nghị, hoặc phàn nàn.
- Admit (thừa nhận):
- Direct: He said, “Yes, I stole the money.”
- Indirect: He admitted stealing the money.
- Deny (phủ nhận):
- Direct: She said, “No, I didn’t see anything.”
- Indirect: She denied seeing anything.
- Suggest (đề nghị):
- Direct: He said, “Let’s go to the beach.”
- Indirect: He suggested going to the beach.
- Insist on (khăng khăng):
- Direct: She said, “I must pay for the meal.”
- Indirect: She insisted on paying for the meal.
- Apologize for (xin lỗi về):
- Direct: He said, “I’m sorry I was late.”
- Indirect: He apologized for being late.
- Complain about (phàn nàn về):
- Direct: She said, “This service is terrible.”
- Indirect: She complained about the terrible service.
- Blame (đổ lỗi):
- Direct: He said, “You are responsible for the mistake.”
- Indirect: He blamed me for the mistake.
- Congratulate (chúc mừng):
- Direct: He said, “Congratulations on winning the award!”
- Indirect: He congratulated me on winning the award.
- Accuse of (buộc tội):
- Direct: She said, “You stole my pen!”
- Indirect: She accused me of stealing her pen.
- Praise for (khen ngợi):
- Direct: The teacher said, “Good job on finishing your project!”
- Indirect: The teacher praised me for finishing my project.
Với that clause (inform, explain, promise, warn, remind, agree, etc.)
Nhiều động từ tường thuật có thể được theo sau bởi một mệnh đề that (có thể lược bỏ), đặc biệt khi tường thuật các thông tin, lời giải thích, lời hứa, cảnh báo, hoặc nhắc nhở. Các động từ này thường mang tính chất thông báo hơn.
- Inform (thông báo):
- Direct: He said, “The train is delayed.”
- Indirect: He informed us that the train was delayed.
- Explain (giải thích):
- Direct: She said, “The reason is complicated.”
- Indirect: She explained that the reason was complicated.
- Promise (hứa): (Cũng có thể dùng với to V)
- Direct: He said, “I will definitely come.”
- Indirect: He promised that he would definitely come.
- Warn (cảnh báo):
- Direct: She said, “Be careful! The road is slippery.”
- Indirect: She warned that the road was slippery.
- Remind (nhắc nhở):
- Direct: He said, “Don’t forget! The deadline is Friday.”
- Indirect: He reminded me that the deadline was Friday.
- Agree (đồng ý): (Cũng có thể dùng với to V)
- Direct: They said, “We believe that you are right.”
- Indirect: They agreed that I was right.
- Announce (thông báo):
- Direct: The company said, “The new product will be launched next month.”
- Indirect: The company announced that the new product would be launched the following month.
- Claim (tuyên bố):
- Direct: He said, “I am innocent.”
- Indirect: He claimed that he was innocent.
- Confirm (xác nhận):
- Direct: She said, “Yes, the meeting is at 2 PM.”
- Indirect: She confirmed that the meeting was at 2 PM.
- Deny (phủ nhận): (Cũng có thể dùng với V-ing)
- Direct: He said, “I did not do it.”
- Indirect: He denied that he had done it.
Với O + to V (advise, warn, order, remind, persuade, enable, etc.)
Một số động từ tường thuật yêu cầu có tân ngữ trực tiếp (người nhận hành động) trước khi sử dụng cấu trúc to V, thường dùng để tường thuật các lời khuyên, cảnh báo, mệnh lệnh, nhắc nhở hoặc thuyết phục.
- Advise (khuyên bảo):
- Direct: He said to me, “You should study harder.”
- Indirect: He advised me to study harder.
- Warn (cảnh báo):
- Direct: She said to him, “Don’t touch the wet paint!”
- Indirect: She warned him not to touch the wet paint.
- Order (ra lệnh):
- Direct: The captain said to the soldiers, “Attack!”
- Indirect: The captain ordered the soldiers to attack.
- Remind (nhắc nhở):
- Direct: He said to me, “Don’t forget your appointment.”
- Indirect: He reminded me not to forget my appointment.
- Persuade (thuyết phục):
- Direct: She said to him, “Please come with us.”
- Indirect: She persuaded him to come with them.
- Ask (yêu cầu):
- Direct: He said to me, “Can you help me?”
- Indirect: He asked me to help him.
- Tell (bảo):
- Direct: She said to him, “Go away!”
- Indirect: She told him to go away.
- Forbid (cấm):
- Direct: The sign said, “No parking here.”
- Indirect: The sign forbade drivers to park there.
- Encourage (khuyến khích):
- Direct: The coach said, “Keep practicing!”
- Indirect: The coach encouraged them to keep practicing.
- Invite (mời):
- Direct: He said to me, “Would you like to have dinner?”
- Indirect: He invited me to have dinner.
Việc chọn đúng động từ tường thuật đặc biệt sẽ không chỉ giúp bạn truyền đạt thông tin một cách chính xác mà còn làm phong phú thêm vốn từ vựng và kỹ năng sử dụng câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh. Hãy luyện tập thường xuyên để làm quen với các cấu trúc này.
Phân biệt câu nói gián tiếp và câu trực tiếp: Khi nào dùng gì?
Việc lựa chọn giữa câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh và câu nói trực tiếp không chỉ đơn thuần là vấn đề ngữ pháp mà còn phụ thuộc vào ngữ cảnh, mục đích giao tiếp và phong cách viết. Cả hai đều có vai trò riêng và việc hiểu rõ sự khác biệt giúp bạn sử dụng ngôn ngữ một cách hiệu quả hơn.
Sự khác biệt về mục đích, ngữ cảnh:
Ví dụ minh họa sự khác biệt và lựa chọn:
- Scenario 1: Kể lại một câu chuyện hấp dẫn:
- Direct: John suddenly shouted, “Look out! A car is coming!” (Tạo kịch tính, cảm giác trực tiếp)
- Indirect: John suddenly shouted for me to look out because a car was coming. (Tường thuật lại, ít kịch tính hơn nhưng mạch lạc)
- Scenario 2: Trích dẫn một phát biểu quan trọng:
- Direct: The CEO stated, “Our company will invest heavily in sustainable technology next year.” (Nhấn mạnh sự chính xác và quyền lực của lời nói)
- Indirect: The CEO stated that their company would invest heavily in sustainable technology the following year. (Tóm tắt thông tin, dùng trong báo cáo)
- Scenario 3: Kể lại một cuộc trò chuyện hàng ngày:
- Direct: My friend said, “I’m going to the gym now. Do you want to join me?“
- Indirect: My friend told me that she was going to the gym then and asked if I wanted to join her. (Phù hợp hơn cho việc kể lại cuộc trò chuyện sau đó)
Lưu ý về dấu câu:
- Câu trực tiếp: Dấu phẩy (,) được dùng để ngăn cách mệnh đề tường thuật với lời nói trực tiếp, và lời nói trực tiếp được đặt trong dấu ngoặc kép (” “). Dấu chấm, hỏi, than nằm trong dấu ngoặc kép.
- He said, “I am tired.”
- She asked, “Are you ready?”
- Câu gián tiếp: Không có dấu ngoặc kép. Dấu chấm, hỏi, than của câu gốc biến mất và thường kết thúc bằng dấu chấm (.). Trật tự từ thay đổi thành câu trần thuật.
- He said that he was tired.
- She asked if I was ready.
Việc lựa chọn giữa câu trực tiếp và câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh là một kỹ năng giao tiếp linh hoạt. Khi cần sự chính xác tuyệt đối, sự sống động, hãy dùng câu trực tiếp. Khi cần sự mạch lạc, khách quan, và tóm tắt, câu gián tiếp là lựa chọn tối ưu.
Các lỗi thường gặp khi sử dụng câu nói gián tiếp và cách khắc phục
Mặc dù câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh là một cấu trúc ngữ pháp mạnh mẽ, nhưng việc sử dụng nó cũng dễ mắc phải những lỗi cơ bản. Nhận biết và khắc phục những lỗi này sẽ giúp bạn nâng cao đáng kể độ chính xác và tự nhiên trong giao tiếp tiếng Anh của mình.
Quên lùi thì
Đây là lỗi phổ biến nhất. Nhiều người thường quên lùi thì của động từ khi động từ tường thuật ở quá khứ.
- Lỗi thường gặp: He said that he is hungry. (Thì hiện tại đơn vẫn giữ nguyên)
- Đúng: He said that he was hungry. (Hiện tại đơn lùi thành quá khứ đơn)
- Cách khắc phục: Luôn kiểm tra động từ tường thuật. Nếu nó ở thì quá khứ (said, told, asked, etc.), hãy nhớ lùi thì của động từ trong mệnh đề gián tiếp. Nắm vững bảng lùi thì.
Không thay đổi trạng từ, đại từ
Lỗi này xảy ra khi người học quên điều chỉnh các đại từ nhân xưng, tính từ sở hữu hoặc trạng từ chỉ thời gian/địa điểm để phù hợp với ngữ cảnh của câu gián tiếp.
- Lỗi thường gặp: She told me that she would meet you tomorrow. (Đại từ “you” và trạng từ “tomorrow” chưa được đổi)
- Đúng: She told me that she would meet me the next day.
- Cách khắc phục: Sau khi lùi thì, bước tiếp theo là xem xét lại tất cả các đại từ (I, you, my, your, we, our) và các trạng từ chỉ thời gian/địa điểm (now, today, here, tomorrow, yesterday) và thay đổi chúng cho phù hợp với người và thời điểm tường thuật.
Sai cấu trúc câu hỏi gián tiếp (đảo ngữ)
Khi chuyển câu hỏi sang gián tiếp, nhiều người vẫn giữ cấu trúc đảo ngữ của câu hỏi trực tiếp.
- Lỗi thường gặp: He asked what was I doing. (Vẫn đảo ngữ “was I”)
- Đúng: He asked what I was doing. (Trật tự từ như câu trần thuật: Chủ ngữ + Động từ)
- Cách khắc phục: Nhớ rằng câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh luôn tuân theo trật tự từ của câu trần thuật (S + V) sau từ nối (if/whether/Wh-word), và không có dấu hỏi chấm ở cuối.
Nhầm lẫn động từ tường thuật
Sử dụng sai động từ tường thuật hoặc sai cấu trúc theo sau động từ đó. Ví dụ, dùng “said” với tân ngữ mà không có “to”, hoặc dùng “suggest” với to V.
- Lỗi thường gặp: She said me that she was leaving. (Sai cấu trúc “said me”)
- Đúng: She told me that she was leaving. (Hoặc She said that she was leaving.)
- Lỗi thường gặp: He suggested to go out. (Sai cấu trúc “suggested to go”)
- Đúng: He suggested going out. (Hoặc He suggested that they should go out.)
- Cách khắc phục: Học thuộc các cấu trúc đi kèm với các động từ tường thuật phổ biến (say, tell, ask, advise, suggest, promise, deny, etc.) và biết khi nào cần tân ngữ, khi nào dùng to V, khi nào dùng V-ing hay that clause.
Không loại bỏ dấu ngoặc kép và dấu chấm hỏi/than
Đây là lỗi định dạng cơ bản nhưng cũng thường xuyên xảy ra.
- Lỗi thường gặp: He said, “I am tired.”
- Đúng: He said that he was tired.
- Cách khắc phục: Luôn nhớ rằng khi chuyển sang câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh, dấu ngoặc kép, dấu hỏi chấm và dấu chấm than đều bị loại bỏ, và câu kết thúc bằng dấu chấm.
Bằng cách nhận thức và chủ động khắc phục những lỗi này, bạn sẽ dần hoàn thiện kỹ năng sử dụng câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh của mình, giúp giao tiếp trở nên tự tin và chuyên nghiệp hơn.
Thực hành: 200+ mẫu câu nói gián tiếp thông dụng trong tiếng Anh
Để thành thạo câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh, việc luyện tập với nhiều ví dụ đa dạng là vô cùng cần thiết. Dưới đây là hơn 200 mẫu câu được chia theo các chủ đề phổ biến, giúp bạn củng cố kiến thức và làm quen với cách áp dụng các quy tắc đã học.
1. Mẫu câu Gián tiếp về Cuộc sống Hàng ngày
- Direct: She said, “I’m going to the store.”Indirect: She said that she was going to the store.
- Direct: He told me, “I have a lot of work today.”Indirect: He told me that he had a lot of work that day.
- Direct: My mother asked, “Did you eat breakfast?”Indirect: My mother asked if I had eaten breakfast.
- Direct: My father said, “I will be home late tonight.”Indirect: My father said that he would be home late that night.
- Direct: The neighbor said, “The weather is lovely.”Indirect: The neighbor said that the weather was lovely.
- Direct: My friend asked, “Can you lend me some money?”Indirect: My friend asked if I could lend him some money.
- Direct: She said, “I finished my chores.”Indirect: She said that she had finished her chores.
- Direct: He said, “I need to buy groceries.”Indirect: He said that he needed to buy groceries.
- Direct: They said, “We are going on vacation next month.”Indirect: They said that they were going on vacation the following month.
- Direct: The child said, “I want ice cream.”Indirect: The child said that he wanted ice cream.
- Direct: She told him, “I will call you later.”Indirect: She told him that she would call him later.
- Direct: He asked, “Where did you go yesterday?”Indirect: He asked where I had gone the day before.
- Direct: My sister said, “I love this song.”Indirect: My sister said that she loved that song.
- Direct: The postman said, “You have a package.”Indirect: The postman said that I had a package.
- Direct: She reminded me, “Don’t forget your keys!”Indirect: She reminded me not to forget my keys.
- Direct: He complained, “The traffic is terrible.”Indirect: He complained that the traffic was terrible.
- Direct: They asked, “What time is the movie?”Indirect: They asked what time the movie was.
- Direct: She promised, “I will be on time.”Indirect: She promised to be on time.
- Direct: He advised me, “You should get some rest.”Indirect: He advised me to get some rest.
- Direct: My friend said, “I saw your brother at the park.”Indirect: My friend said that she had seen my brother at the park.
2. Mẫu câu Gián tiếp về Tình yêu & Quan hệ
- Direct: He said to her, “I love you.”Indirect: He told her that he loved her.
- Direct: She asked him, “Will you marry me?”Indirect: She asked him if he would marry her.
- Direct: He said, “I’m thinking of you.”Indirect: He said that he was thinking of her.
- Direct: She whispered, “You’re my everything.”Indirect: She whispered that he was her everything.
- Direct: They said, “We are so happy together.”Indirect: They said that they were so happy together.
- Direct: He confessed, “I miss you every day.”Indirect: He confessed that he missed her every day.
- Direct: She asked, “Do you believe in love at first sight?”Indirect: She asked if I believed in love at first sight.
- Direct: My girlfriend said, “I want to spend more time with you.”Indirect: My girlfriend said that she wanted to spend more time with me.
- Direct: He proposed, “Let’s build a future together.”Indirect: He proposed building a future together.
- Direct: She told him, “I can’t imagine life without you.”Indirect: She told him that she couldn’t imagine life without him.
- Direct: He said, “You are beautiful.”Indirect: He said that she was beautiful.
- Direct: She asked, “Are you seeing anyone?”Indirect: She asked if I was seeing anyone.
- Direct: My husband said, “I’ll always be there for you.”Indirect: My husband said that he would always be there for me.
- Direct: She reassured him, “Everything will be alright.”Indirect: She reassured him that everything would be alright.
- Direct: He apologized, “I’m sorry for hurting you.”Indirect: He apologized for hurting her.
- Direct: She promised, “I’ll never leave you.”Indirect: She promised that she would never leave him.
- Direct: He confessed, “I made a mistake.”Indirect: He confessed that he had made a mistake.
- Direct: She wondered, “Does he really love me?”Indirect: She wondered if he really loved her.
- Direct: My partner said, “We need to talk.”Indirect: My partner said that we needed to talk.
- Direct: He insisted, “I will always cherish you.”Indirect: He insisted on always cherishing her.
3. Mẫu câu Gián tiếp về Công việc & Học tập
- Direct: The manager said, “The deadline is Friday.”Indirect: The manager said that the deadline was Friday.
- Direct: My professor asked, “Have you submitted your assignment?”Indirect: My professor asked if I had submitted my assignment.
- Direct: He said, “I’m working on a new project.”Indirect: He said that he was working on a new project.
- Direct: She told her colleague, “I’ll help you with that report.”Indirect: She told her colleague that she would help him with that report.
- Direct: The teacher said, “Open your books to page 20.”Indirect: The teacher told the students to open their books to page 20.
- Direct: He complained, “My workload is too heavy.”Indirect: He complained that his workload was too heavy.
- Direct: She asked, “When is the exam?”Indirect: She asked when the exam was.
- Direct: My boss said, “We need to increase sales.”Indirect: My boss said that they needed to increase sales.
- Direct: He advised me, “You should prepare well for the interview.”Indirect: He advised me to prepare well for the interview.
- Direct: The student said, “I don’t understand this concept.”Indirect: The student said that he didn’t understand that concept.
- Direct: The lecturer said, “The next class is on Tuesday.”Indirect: The lecturer said that the next class was on Tuesday.
- Direct: My classmate asked, “Can you explain this again?”Indirect: My classmate asked if I could explain that again.
- Direct: He announced, “I’ve got a promotion!”Indirect: He announced that he had got a promotion.
- Direct: She worried, “I might fail the test.”Indirect: She worried that she might fail the test.
- Direct: The HR manager said, “Your application was successful.”Indirect: The HR manager said that my application had been successful.
- Direct: He suggested, “Let’s review the notes together.”Indirect: He suggested reviewing the notes together.
- Direct: She asked, “Who is leading this project?”Indirect: She asked who was leading that project.
- Direct: My professor said, “Plagiarism will not be tolerated.”Indirect: My professor said that plagiarism would not be tolerated.
- Direct: He confided, “I’m struggling with this course.”Indirect: He confided that he was struggling with that course.
- Direct: She promised, “I’ll submit the report on time.”Indirect: She promised to submit the report on time.
4. Mẫu câu Gián tiếp về Du lịch & Khám phá
- Direct: She said, “I’m going to travel around the world.”Indirect: She said that she was going to travel around the world.
- Direct: He asked, “Have you ever been to Paris?”Indirect: He asked if I had ever been to Paris.
- Direct: They said, “We visited many ancient ruins.”Indirect: They said that they had visited many ancient ruins.
- Direct: The guide said, “The tour starts at 9 AM.”Indirect: The guide said that the tour started at 9 AM.
- Direct: She exclaimed, “What a breathtaking view!”Indirect: She exclaimed that it was a breathtaking view.
- Direct: He advised us, “Don’t forget your passports.”Indirect: He advised us not to forget our passports.
- Direct: I asked, “Where is the nearest subway station?”Indirect: I asked where the nearest subway station was.
- Direct: She said, “I’m planning a trip to Vietnam next year.”Indirect: She said that she was planning a trip to Vietnam the following year.
- Direct: They wondered, “Is it safe to hike here?”Indirect: They wondered if it was safe to hike there.
- Direct: The tourist said, “I want to try local food.”Indirect: The tourist said that he wanted to try local food.
- Direct: He asked, “How much does the ticket cost?”Indirect: He asked how much the ticket cost.
- Direct: She told him, “I will send you postcards.”Indirect: She told him that she would send him postcards.
- Direct: They complained, “The hotel service was poor.”Indirect: They complained that the hotel service had been poor.
- Direct: He suggested, “Let’s explore the old town.”Indirect: He suggested exploring the old town.
- Direct: She informed us, “The flight has been delayed.”Indirect: She informed us that the flight had been delayed.
- Direct: The local said, “You should visit the temple.”Indirect: The local said that I should visit the temple.
- Direct: He said, “I’ve never seen anything like this before.”Indirect: He said that he had never seen anything like that before.
- Direct: She asked, “When are you returning?”Indirect: She asked when I was returning.
- Direct: My friend said, “I’m having a great time here.”Indirect: My friend said that he was having a great time there.
- Direct: He warned, “Be careful of pickpockets.”Indirect: He warned me to be careful of pickpockets.
5. Mẫu câu Gián tiếp về Sức khỏe & Thể thao
- Direct: The doctor said, “You should drink more water.”Indirect: The doctor advised me to drink more water.
- Direct: She said, “I’m feeling unwell.”Indirect: She said that she was feeling unwell.
- Direct: He asked, “Did you go to the gym today?”Indirect: He asked if I had gone to the gym that day.
- Direct: My coach said, “Practice makes perfect.”Indirect: My coach said that practice makes perfect.
- Direct: She promised, “I will start eating healthier.”Indirect: She promised to start eating healthier.
- Direct: He said, “I need to lose weight.”Indirect: He said that he needed to lose weight.
- Direct: The nurse told me, “Take your medicine regularly.”Indirect: The nurse told me to take my medicine regularly.
- Direct: They said, “We are training for a marathon.”Indirect: They said that they were training for a marathon.
- Direct: She asked, “How often do you exercise?”Indirect: She asked how often I exercised.
- Direct: He complained, “My back hurts.”Indirect: He complained that his back hurt.
- Direct: The physiotherapist said, “Do these stretches daily.”Indirect: The physiotherapist told me to do those stretches daily.
- Direct: She announced, “I’ve started yoga.”Indirect: She announced that she had started yoga.
- Direct: He wondered, “Is running good for my knees?”Indirect: He wondered if running was good for his knees.
- Direct: My friend said, “I’m trying to cut down on sugar.”Indirect: My friend said that she was trying to cut down on sugar.
- Direct: She warned, “Don’t lift heavy weights without proper form.”Indirect: She warned me not to lift heavy weights without proper form.
- Direct: He said, “I feel much better after the rest.”Indirect: He said that he felt much better after the rest.
- Direct: They asked, “What’s your favorite sport?”Indirect: They asked what my favorite sport was.
- Direct: She encouraged him, “Don’t give up on your fitness goals.”Indirect: She encouraged him not to give up on his fitness goals.
- Direct: He explained, “A balanced diet is crucial.”Indirect: He explained that a balanced diet was crucial.
- Direct: She suggested, “Let’s go for a walk.”Indirect: She suggested going for a walk.
6. Mẫu câu Gián tiếp về Công nghệ & Mạng xã hội
- Direct: He said, “I bought a new smartphone.”Indirect: He said that he had bought a new smartphone.
- Direct: She asked, “What’s your Wi-Fi password?”Indirect: She asked what my Wi-Fi password was.
- Direct: My brother said, “I downloaded a new app.”Indirect: My brother said that he had downloaded a new app.
- Direct: The technician said, “Your computer has a virus.”Indirect: The technician said that my computer had a virus.
- Direct: She posted, “Having a great day!”Indirect: She posted that she was having a great day.
- Direct: He asked, “Did you see my latest post?”Indirect: He asked if I had seen his latest post.
- Direct: My friend said, “I’m addicted to social media.”Indirect: My friend said that he was addicted to social media.
- Direct: She warned, “Don’t share too much personal information online.”Indirect: She warned me not to share too much personal information online.
- Direct: He suggested, “Let’s watch a movie on Netflix.”Indirect: He suggested watching a movie on Netflix.
- Direct: The IT support said, “Restart your router.”Indirect: The IT support told me to restart my router.
- Direct: She asked, “How do I upload a video?”Indirect: She asked how to upload a video.
- Direct: He said, “I need to update my software.”Indirect: He said that he needed to update his software.
- Direct: My daughter said, “I want a new tablet.”Indirect: My daughter said that she wanted a new tablet.
- Direct: The company announced, “We are launching a new feature.”Indirect: The company announced that they were launching a new feature.
- Direct: He complained, “My internet is too slow.”Indirect: He complained that his internet was too slow.
- Direct: She asked, “Are you on Instagram?”Indirect: She asked if I was on Instagram.
- Direct: He said, “I’m trying to reduce my screen time.”Indirect: He said that he was trying to reduce his screen time.
- Direct: She explained, “This AI tool can write articles.”Indirect: She explained that that AI tool could write articles.
- Direct: He wondered, “Will robots take over the world?”Indirect: He wondered if robots would take over the world.
- Direct: My friend advised, “Back up your data regularly.”Indirect: My friend advised me to back up my data regularly.
7. Mẫu câu Gián tiếp về Mua sắm & Tiêu dùng
- Direct: She said, “I’m going shopping.”Indirect: She said that she was going shopping.
- Direct: He asked, “How much does this cost?”Indirect: He asked how much that cost.
- Direct: My mother said, “I need a new pair of shoes.”Indirect: My mother said that she needed a new pair of shoes.
- Direct: The salesman said, “This item is on sale.”Indirect: The salesman said that that item was on sale.
- Direct: She complained, “The size is too small.”Indirect: She complained that the size was too small.
- Direct: He said, “I’ll pay by credit card.”Indirect: He said that he would pay by credit card.
- Direct: She asked, “Do you have this in blue?”Indirect: She asked if they had that in blue.
- Direct: The customer asked, “Can I return this?”Indirect: The customer asked if he could return that.
- Direct: He said, “I’m looking for a gift for my sister.”Indirect: He said that he was looking for a gift for his sister.
- Direct: She advised, “You should compare prices before buying.”Indirect: She advised me to compare prices before buying.
- Direct: The cashier said, “Your total is $50.”Indirect: The cashier said that my total was $50.
- Direct: He promised, “I’ll buy you dinner.”Indirect: He promised to buy me dinner.
- Direct: She wondered, “Is this brand reliable?”Indirect: She wondered if that brand was reliable.
- Direct: My friend said, “I found a great deal online.”Indirect: My friend said that he had found a great deal online.
- Direct: He warned, “Don’t spend all your money.”Indirect: He warned me not to spend all my money.
- Direct: She said, “I can’t afford this.”Indirect: She said that she couldn’t afford that.
- Direct: They asked, “Which color do you prefer?”Indirect: They asked which color I preferred.
- Direct: She insisted, “I want the red one.”Indirect: She insisted on wanting the red one.
- Direct: He suggested, “Let’s check out the new mall.”Indirect: He suggested checking out the new mall.
- Direct: The child cried, “I want that toy!”Indirect: The child cried that he wanted that toy.
8. Mẫu câu Gián tiếp về Ý kiến & Cảm xúc
- Direct: She said, “I think he’s right.”Indirect: She said that she thought he was right.
- Direct: He asked, “What do you think about this?”Indirect: He asked what I thought about that.
- Direct: My friend said, “I’m so excited for the concert!”Indirect: My friend said that she was so excited for the concert.
- Direct: She complained, “I’m really annoyed.”Indirect: She complained that she was really annoyed.
- Direct: He confessed, “I’m feeling a bit sad today.”Indirect: He confessed that he was feeling a bit sad that day.
- Direct: She said, “I disagree with that statement.”Indirect: She said that she disagreed with that statement.
- Direct: They expressed, “We are truly grateful.”Indirect: They expressed that they were truly grateful.
- Direct: He argued, “That’s not fair!”Indirect: He argued that that was not fair.
- Direct: She wondered, “Why is he so quiet?”Indirect: She wondered why he was so quiet.
- Direct: My colleague said, “I’m optimistic about the future.”Indirect: My colleague said that she was optimistic about the future.
- Direct: He admitted, “I was wrong.”Indirect: He admitted that he had been wrong.
- Direct: She denied, “I didn’t say that.”Indirect: She denied saying that.
- Direct: He exclaimed, “What a relief!”Indirect: He exclaimed that it was a relief.
- Direct: She smiled and said, “I’m happy for you.”Indirect: She smiled and said that she was happy for me.
- Direct: He sighed, “I’m exhausted.”Indirect: He sighed that he was exhausted.
- Direct: She praised, “Your work is excellent.”Indirect: She praised my work as excellent.
- Direct: He criticized, “The plan has many flaws.”Indirect: He criticized that the plan had many flaws.
- Direct: She apologized, “I’m sorry for my mistake.”Indirect: She apologized for her mistake.
- Direct: He reassured me, “Don’t worry, everything will be fine.”Indirect: He reassured me not to worry and that everything would be fine.
- Direct: She stated, “My opinion is firm.”Indirect: She stated that her opinion was firm.
9. Mẫu câu Gián tiếp trong Tình huống Giao tiếp Khác
- Direct: The news anchor said, “Good evening.”Indirect: The news anchor greeted the audience good evening.
- Direct: He asked, “Excuse me, where is the restroom?”Indirect: He asked where the restroom was.
- Direct: She replied, “Thank you.”Indirect: She thanked him.
- Direct: He invited, “Would you like to join us for dinner?”Indirect: He invited me to join them for dinner.
- Direct: She congratulated him, “Well done!”Indirect: She congratulated him.
- Direct: He wished me, “Happy birthday!”Indirect: He wished me a happy birthday.
- Direct: She proposed a toast, “To our success!”Indirect: She proposed a toast to their success.
- Direct: He introduced, “This is my friend, Sarah.”Indirect: He introduced Sarah as his friend.
- Direct: She said goodbye, “See you later.”Indirect: She said goodbye and said that she would see me later.
- Direct: He answered the phone, “Hello?”Indirect: He answered the phone.
- Direct: She said, “Could you please pass the salt?”Indirect: She asked me to pass the salt.
- Direct: He warned, “Look out for falling rocks!”Indirect: He warned me to look out for falling rocks.
- Direct: She inquired, “Is there anything else I can do for you?”Indirect: She inquired if there was anything else she could do for me.
- Direct: He confirmed, “Yes, that’s correct.”Indirect: He confirmed that that was correct.
- Direct: She promised, “I’ll keep your secret.”Indirect: She promised to keep my secret.
- Direct: He suggested, “Why don’t we try the new restaurant?”Indirect: He suggested trying the new restaurant.
- Direct: She complained, “It’s too cold in here.”Indirect: She complained that it was too cold in there.
- Direct: He admitted, “I was a bit nervous.”Indirect: He admitted being a bit nervous.
- Direct: She denied, “I never said that.”Indirect: She denied ever saying that.
- Direct: He insisted, “I’ll pay for the meal.”Indirect: He insisted on paying for the meal.
10. Thêm các mẫu câu Gián tiếp khác
- Direct: The sign said, “No smoking.”Indirect: The sign forbade smoking.
- Direct: My neighbour offered, “Can I help you with your bags?”Indirect: My neighbour offered to help me with my bags.
- Direct: She recalled, “I met him years ago.”Indirect: She recalled that she had met him years before.
- Direct: He boasted, “I’m the best in the class.”Indirect: He boasted that he was the best in the class.
- Direct: She muttered, “This is impossible.”Indirect: She muttered that that was impossible.
- Direct: He challenged, “Prove it!”Indirect: He challenged me to prove it.
- Direct: She wondered, “What will happen next?”Indirect: She wondered what would happen next.
- Direct: My colleague recommended, “You should try this coffee shop.”Indirect: My colleague recommended that I try that coffee shop.
- Direct: He advised, “Always follow your dreams.”Indirect: He advised me to always follow my dreams.
- Direct: She apologized for, “I’m sorry for being late.”Indirect: She apologized for being late.
- Direct: He blamed me for, “You caused this problem.”Indirect: He blamed me for causing that problem.
- Direct: She praised me for, “Your presentation was excellent.”Indirect: She praised me for my excellent presentation.
- Direct: He criticized, “The decision was poorly made.”Indirect: He criticized that the decision had been poorly made.
- Direct: She encouraged him, “Keep going, you can do it!”Indirect: She encouraged him to keep going and said that he could do it.
- Direct: He reminded me, “Don’t forget the meeting!”Indirect: He reminded me not to forget the meeting.
- Direct: She agreed, “That’s a good idea.”Indirect: She agreed that that was a good idea.
- Direct: He refused, “I won’t participate.”Indirect: He refused to participate.
- Direct: She threatened, “I’ll report you.”Indirect: She threatened to report me.
- Direct: He decided, “I will travel the world.”Indirect: He decided to travel the world.
- Direct: She demanded, “Tell me the truth!”Indirect: She demanded that I tell her the truth.
- Direct: He exclaimed, “Unbelievable!”Indirect: He exclaimed that it was unbelievable.
- Direct: She muttered, “I hate Mondays.”Indirect: She muttered that she hated Mondays.
- Direct: He stressed, “This is very important.”Indirect: He stressed that that was very important.
- Direct: She whispered, “Don’t tell anyone.”Indirect: She whispered not to tell anyone.
- Direct: He announced, “Dinner is served!”Indirect: He announced that dinner was served.
Với những ví dụ trên, bạn sẽ có một nền tảng vững chắc để thực hành và làm chủ câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh trong nhiều tình huống khác nhau.
Liên kết nội bộ:
Để tìm hiểu thêm về các loại câu nói hay và STT ý nghĩa, bạn có thể truy cập Trường Nguyễn Bỉnh Khiêm.
Trong tiếng Anh, câu nói gián tiếp trong tiếng Anh là một cấu trúc ngữ pháp vô cùng quan trọng, giúp chúng ta truyền tải lại lời nói của người khác một cách mượt mà, phù hợp với ngữ cảnh và thể hiện sự tinh tế trong giao tiếp. Từ việc lùi thì động từ, thay đổi đại từ và trạng từ, đến việc lựa chọn động từ tường thuật đặc biệt, mỗi quy tắc đều góp phần tạo nên sự chính xác cho lời tường thuật. Nắm vững những nguyên tắc này và thường xuyên luyện tập với các mẫu câu đa dạng sẽ giúp bạn tự tin hơn trong việc sử dụng tiếng Anh, cả trong văn viết lẫn giao tiếp hàng ngày. Hãy luôn ghi nhớ rằng việc sử dụng đúng câu nói gián tiếp không chỉ là tuân thủ ngữ pháp mà còn là cách bạn thể hiện sự hiểu biết sâu sắc về ngôn ngữ.


Nội dung được phát triển bởi đội ngũ truongnguyenbinhkhiem.edu.vn với mục đích chia sẻ và tăng trải nghiệm khách hàng. Mọi ý kiến đóng góp xin vui lòng liên hệ tổng đài chăm sóc: 1900 0000 hoặc email: hotro@truongnguyenbinhkhiem.edu.vn